e-commerce
2022 E-Commerce Buzzword Glossary: Top 35 Definitions
Do you know your TTMs from your TCOs? Check out this e-commerce buzzword glossary to be ahead of the game in 2022


Whether you work in e-commerce, are looking to digitize, or even studying the field, you’ve surely come across what we lovingly refer to at Spryker as “e-commerce bullshit bingo”.
Companies and websites throw out buzzwords and acronyms left, right and center (and yes, we know we can sometimes also be a culprit🙈) and just trying to understand what’s possible and what the benefits are can start to feel like running a linguistic marathon.
The most important thing to keep in mind about e-commerce is that it’s constantly evolving. As soon as products, features, or definitions are agreed upon, there’s already a new kid on the block. To help keep on top of this, we’ve created the 2022 E-Commerce Buzzword Glossary with 35 top definitions to keep you informed as we roll into next year.
2022 E-Commerce Buzzword Glossary
A
A/B Testing (also known as Split Testing)
Often used in marketing, A/B or split testing is where you compare two different versions of something – commonly, a web page. You have a control, the original, and a variation. You can then test which version works better, and adjust accordingly. This can be applied to images, copy, pricing, localization, and much much more. For e-commerce, it’s particularly important to have a ‘test and learn’ mindset, especially when launching a new product or in a new market, meaning A/B testing is a vital component.
API (Application Programming Interface)
An API is a set of commands, protocols, functions, and objects that programmers can use to create software or interact with an external system. Take our GLUE API for example, it allows information from the Spryker Cloud Commerce OS back-end to be sent to an external system (a front-end) such as a smartwatch, mobile device, or voice assistant, for instance.
B
Best-of-Breed
Best-of-breed refers to your e-commerce technology stack approach. Best-of-breed means mixing and matching the best vendors or services to perform specific tasks or functions within your technology stack. For example, you might choose a payment gateway vendor like PayPal for your online store, and a Content Management System such as WordPress for your website blog.
Best-of-Suite
Best-of-suite is the opposite approach to best-of-breed. You choose one major application provider and can only pick and choose from the solutions that they provide. There is less flexibility and third-party add-ons are often required to fulfill all business needs.
Brownfield
In the world of urban planning, brownfield refers to any previously developed land. In software development, brownfield means adding or developing new software on top of existing or legacy systems. In e-commerce, a brownfield project might then refer to a project utilizing new software on top of an existing system, or a new project within an existing market.
C
Composable Commerce
A relatively recent term coined by Gartner, Composable Commerce refers to a modular digital commerce approach. This means that businesses can choose best-of-breed solutions to build a customized tech stack that meets their unique business requirements.
CLV (Customer Lifetime Value)
CLV measures just how valuable a customer is to your business – not just on a purchase-by-purchase level, but across the entire potential relationship. For e-commerce businesses, customer retention is vital, therefore CLV is a very important metric to keep on top of.
D
Dropshipping
Dropshipping refers to the method of selling where the seller isn’t in charge of the stock. Rather, the seller purchases the item from a third-party supplier and then has it shipped directly to the customer, meaning the seller never handles the product directly. Dropshipping has revolutionized e-commerce as it allows businesses to scale their product assortment without taking on the inventory risk.
E
Enterprise marketplace
An enterprise marketplace refers to a marketplace where both the operator and third-party merchants sell products on the same platform.

ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
ERP is the process by which companies manage and integrate various important parts of their business, such as inventory management, marketing, finance, etc. Many businesses use software to manage their ERP to keep everything within a single system.
F
FeS (Front-end Enablement Service)
FeS refers to the Spryker solution which allows e-commerce customers to build, test, and launch codeless digital storefronts with a focus on intuitive customer experience.
Fulfillment
E-commerce fulfillment is referring to the process of completing an order, i.e., when a customer orders a product online, you as the merchant then complete the sale, and ensure the product arrives with the customer within the agreed time frame and price point.
G
Gateway (also known as Payment Gateway)
In order to enable customers to buy online, e-commerce providers must be able to authorize credit cards and direct payments. This service is often provided by gateway applications that have been specifically designed for online retailers.
Greenfield
In the world of urban planning, greenfield refers to any land without pre-existing development. In software development, greenfield means developing software in a completely new environment, with no existing legacy code. In e-commerce, a greenfield project might then refer to a project launching a completely new product or in an entirely new market.
H
Headless Commerce
Headless commerce is an e-commerce architecture that allows for a separation between the front-end (customer-facing layer) and the back-end infrastructure (where the shopping cart, product catalog, payment gateway, and other features ordinarily reside). To put it simply, with headless commerce, the front-end is decoupled from the back-end. One great advantage for e-commerce businesses is that it encourages modularity and enables businesses to integrate numerous touchpoints through APIs.

Source: Mika
I
ISS (Infinity Shopping Shelf)
The idea of the e-commerce Infinity Shopping Shelf is that you can offer an unlimited number of products or services because you aren’t held back by the physical shelf space in a brick-and-mortar store. This is particularly relevant in a marketplace model where operators can offer products from third-party merchants to extend their product offering.
Inventory
Inventory is the physical amount of tangible goods, products, or services you offer your customers. One of the benefits of marketplace technology is that you can extend your inventory by working with third-party merchants, without taking on the financial risk of additional stock.
M
Marketplace
In the e-commerce world, a marketplace is an online platform where the operator can allow third-party merchants to sell products or services. Marketplace technology is a great way for businesses to scale while reducing risk, as the operator shares inventory management, fulfillment, etc with third-party merchants.
MOAs (Marketplace Operation Applications)
Gartner defines marketplace operation applications as those which enable existing e-commerce owners to transform their sites into online marketplaces. These applications typically manage vendor onboarding, product catalogs, order routing, order status updates, and vendor compliance with marketplace regulations.
Merchant
In the e-commerce context, a merchant is a seller of products or services in an online shop. A merchant can operate in a stand B2C or B2B shop, or within a marketplace.
Microservices
Microservices are specific services that solve or enable a single business functionality. They tend to be small, and communicate with one another via APIs. They are independent and don’t share data or a platform, for example, so developers can easily update one without disturbing another.
Middleware
Middleware is software that acts as a bridge between two separate programs so they can share data and communicate with one another.
MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
An MVP is a basic or early draft version of a product or service which is released with the intention of gathering feedback for further improvement and development. MVPs are very important in e-commerce as you can use them to test new products or new markets before heavy investment.
Modular Architecture
This approach refers to software architecture that can be built from self-contained modules which are deployed and developed independently. This allows for greater flexibility and speed when adapting to fast market changes.
Source: Xavi Cabrera
Monolithic Architecture
This approach refers to software architecture that is composed in one unified model. Most traditional or historical e-commerce stores were built using monolithic architecture.
P
PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service)
PaaS is a type of cloud platform that delivers application infrastructure capabilities, as a service. Our Spryker Cloud Commerce OS is an example of a PaaS solution, as it allows our customers to develop, run, and manage their Spryker application without the complexity of building, maintaining, or scaling the infrastructure.
PBCs (Packaged Business Capabilities)
Another Gartner-defined term, PBCs are an independent assembly of features grouped into larger clusters, representing a well-defined business capability or functionality. They’re the perfect in-between solution between slow monolithic applications and small, hard-to-manage microservices.
PIM (Product Information Management)
A PIM system is used to manage and distribute data for various sales channels, including e-commerce sites or apps, marketplaces, social media, and more. Examples of what a PIM system manages includes product descriptions and product media files.
POS (Point-of-Sale System)
The POS is where the real transaction takes place between seller and buyer. In an e-commerce environment, the POS is the software that handles the financial and administrative work of running your business, tracking inventory, sales trends, and more.
Pure Marketplace
A pure marketplace is a platform where only third-party merchants sell goods, in comparison to an enterprise marketplace – where the operator is also a seller.
S
SDKs (Software Development Kits)
SDKs are collections of software development tools neatly packaged into installable units. They enable the creation of applications and are normally designed to work with a specific hardware platform or operating system. They are essentially toolkits for your developers.
State Machine
In e-commerce, every item which is ordered then needs to be processed, packed and shipped to the end customer. This can be very complex and looks different for every company. State machines are essentially ‘business process models’ which create a standard way of configuring and executing business processes such as payment, shipping, and more to ensure uniformity.
T
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO is a very common term in e-commerce, generally referring to the total long-term cost of a project, i.e. both purchase price and costs of operation. When comparing services or vendors, those with the lower total cost of ownership represent the best value in the long run.
TTM/T2M (Time to Market)
Quite simply, TTM is the total length of time it takes from a product or service being conceived until it is commercially available. This term is often used in conjunction with MVP (Minimum Viable Product) as releasing a pared-back version of a product allows for a faster TTM.
U
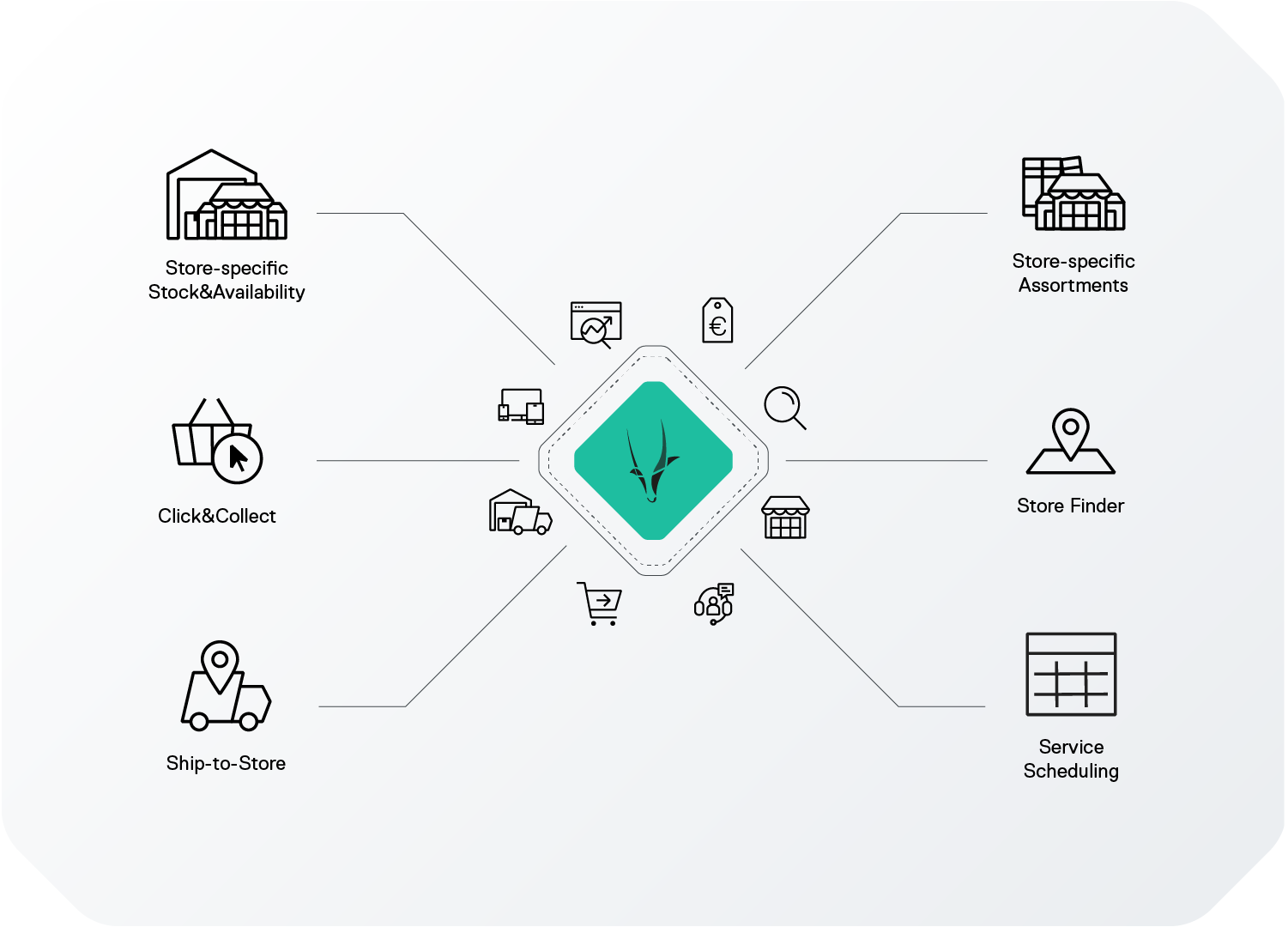
Unified Commerce
Unified commerce is all about offering your customers consistent online and offline experiences, so no matter which channel they are shopping through, they feel the continuity of the brand. Unified commerce typically comes hand-in-hand with a variety of sales channels, such as in-store shopping, Click&Collect, BOPIS (Buy Online Pick-up In-Store), home delivery, and more.
Want to learn more about the lingo?
Phew, we got there. We hope this e-commerce buzzword glossary has been helpful. There are a lot of concepts to wrap your head around, especially if you’re new to digitization. However, as mentioned earlier, the world of e-commerce is accelerating and evolving rapidly, so one of the most important concepts to get to grips with is the idea of the MVP (minimum viable product). To learn more, check out our MVP guide – explaining exactly how they’re a solution for rapidly changing markets.
